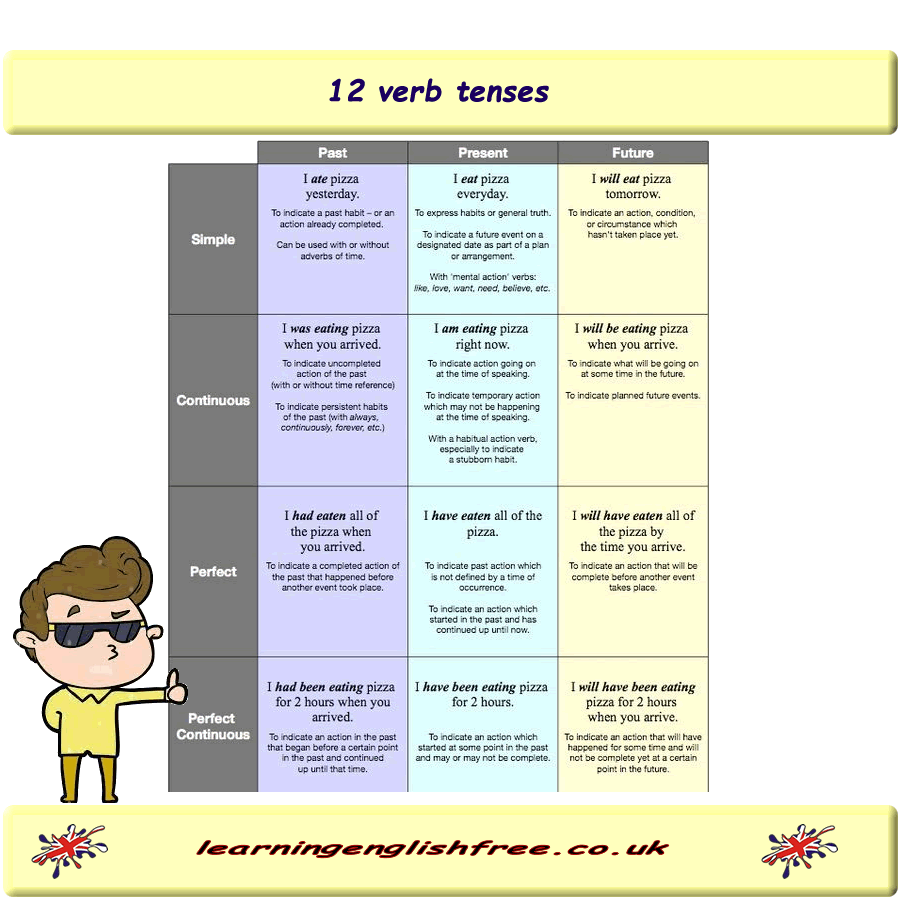
Introduction to the 12 Verb Tenses in English
Useful Vocabulary:
- Tense
- Action
- Timeframe
- Continuous
- Perfect
Now, let us look at examples of how to use each 12-verb tenses in English.
Simple Present Tense: Describes regular actions or general truths in the present.
- She works at the library.
- They eat dinner at 6 pm.
- He speaks English fluently.
- I live in a small town.
- The sun rises in the east.
Present Continuous Tense: Describes actions happening right now.
- She is reading a book.
- They are playing soccer.
- He is writing a report.
- I am cooking dinner.
- The kids are watching TV.
Simple Past Tense: Describes actions that happened in the past.
- She danced at the party last night.
- They visited Paris last summer.
- He worked at that company for five years.
- I watched a movie yesterday.
- We ate pizza for lunch.
Past Continuous Tense: Describes ongoing actions in the past.
- She was singing when I called.
- They were studying when the phone rang.
- He was working late yesterday.
- I was reading a novel all evening.
- We were driving to the beach when it started raining.
Simple Future Tense: Describes actions that will happen in the future.
- She will dance at the recital tomorrow.
- They will travel to Europe next summer.
- He will complete the project next week.
- I will meet you at 4 pm.
- We will eat at the new restaurant.
Future Continuous Tense: Describes ongoing future actions.
- She will be dancing at the party tomorrow night.
- They will be studying all evening.
- He will be working on the project at that time.
- We will be travelling to Europe next year.
- He will be driving to the airport in the morning.
Present Perfect Tense: Describes actions that started in the past and continue into the present or have just been completed.
- She has danced in many competitions.
- They have visited Paris several times.
- I have worked on this project for weeks.
- We have eaten at that restaurant before.
- He has read that book already.
Past Perfect Tense: Describes actions completed before a certain point in the past.
- She had danced before the music stopped.
- They had already left when I arrived.
- I had finished my homework before dinner.
- We had visited the museum by the time it closed.
- He had already left for work when I called.
Future Perfect Tense: Describes actions that will be completed before a certain point in the future.
- She will have danced for ten years by next summer.
- They will have finished their project by December.
- I will have completed my degree by next year.
- We will have eaten by the time the movie starts.
- He will have read the entire book by next week.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense: Describes actions that started in the past, continue into the present, and may continue into the future.
- She has been dancing for hours.
- They have been working on this project all day.
- I have been studying for the exam since morning.
- We have been waiting for a long time.
- He has been practising the piano for weeks.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Describes ongoing actions in the past, completed before a certain point in the past.
- She had been dancing for an hour before I arrived.
- They had been studying all day before the exam.
- I had been working at that company for five years before I quit.
- We had been living in that house for a decade before we moved.
- He had been exercising for an hour before he felt tired.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense: Describes actions that will be ongoing in the future and will be completed before a certain point in the future.
- She will have been dancing for two hours by the time the party ends.
- They will have been working for a week by the project's deadline.
- I will have been studying for hours when the exam starts.
- We will have been waiting for an hour when the bus arrives.
- He will have been jogging for an hour before he takes a break.
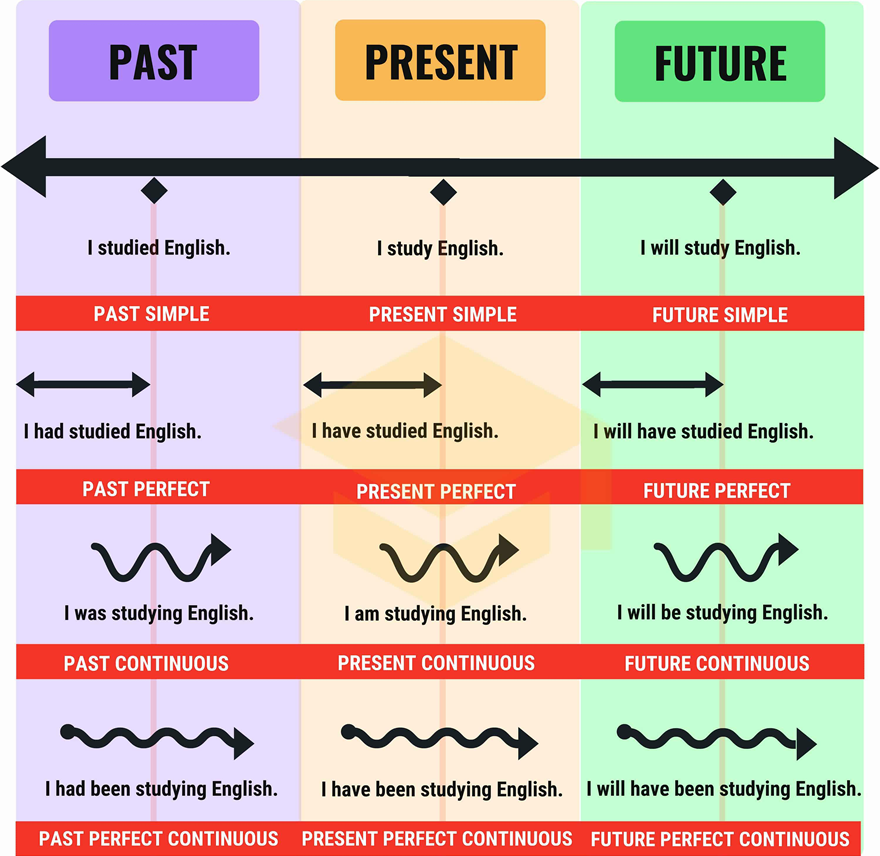
What are the 12 tenses used for?
The 12 tenses in English help us talk about time - when things happen, how long they last, and whether they are finished or still going on. We need to learn them to be clear about these different times. Here's why they are important in simple English:
-
Simple Present: We use this to talk about things that happen regularly or facts. Like, "I eat breakfast every morning."
-
Present Continuous: This is for things happening right now. Like, "I am eating breakfast now."
-
Simple Past: We use it to talk about things that happened and finished in the past. Like, "I ate breakfast."
-
Past Continuous: This is for things that were happening at a specific time in the past. Like, "I was eating breakfast at 7 am."
-
Simple Future: We use this to talk about things that will happen in the future. Like, "I will eat breakfast tomorrow."
-
Future Continuous: This is for things that will be happening at a specific time in the future. Like, "I will be eating breakfast at 7 am tomorrow."
-
Present Perfect: We use this for things that started in the past and are still happening or just finished. Like, "I have eaten breakfast" (it means I finished recently).
-
Past Perfect: This is for things that were finished before another time in the past. Like, "I had eaten breakfast before I left the house."
-
Future Perfect: We use this for things that will be finished before a specific time in the future. Like, "I will have eaten breakfast by 8 am."
-
Present Perfect Continuous: This is for things that started in the past and are still happening now or have just stopped. Like, "I have been eating breakfast" (it means I just stopped).
-
Past Perfect Continuous: This is for things that were happening before and until another time in the past. Like, "I had been eating breakfast when you called."
-
Future Perfect Continuous: We use this for things that will be happening until a specific time in the future. Like, "I will have been eating breakfast for an hour by the time you arrive."
Learning the 12 verb tenses in English accurately helps to communicate precise timeframes in speech and writing.
Summary and Takeaways
- Understanding Tenses: The 12 verb tenses are fundamental in expressing time in English, each serving a unique purpose.
- Key Phrases: Remember phrases like "was doing" for Past Continuous or "will have been doing" for Future Perfect Continuous.
- Memorization Tips: Associate each tense with a specific time frame and action. Practice forming sentences using each tense.
- Real-Life Application: Pay attention to how these tenses are used in everyday conversations, news, and literature.
- Further Learning: Explore more examples and practice exercises on our website and Facebook page.
