The Essence of Verbs in English
Verbs are the backbone of the English language, serving as the main building blocks of our sentences. They provide not only action but also a sense of being, allowing us to express what we do, think, feel, and more. This lesson delves into the various types of verbs - from action to auxiliary, regular to irregular, and beyond. By understanding these categories, learners will enhance their ability to communicate effectively and enrich their linguistic repertoire. Let's embark on this journey to demystify verbs, armed with useful vocabulary and practical examples to ensure a solid grasp of each type.
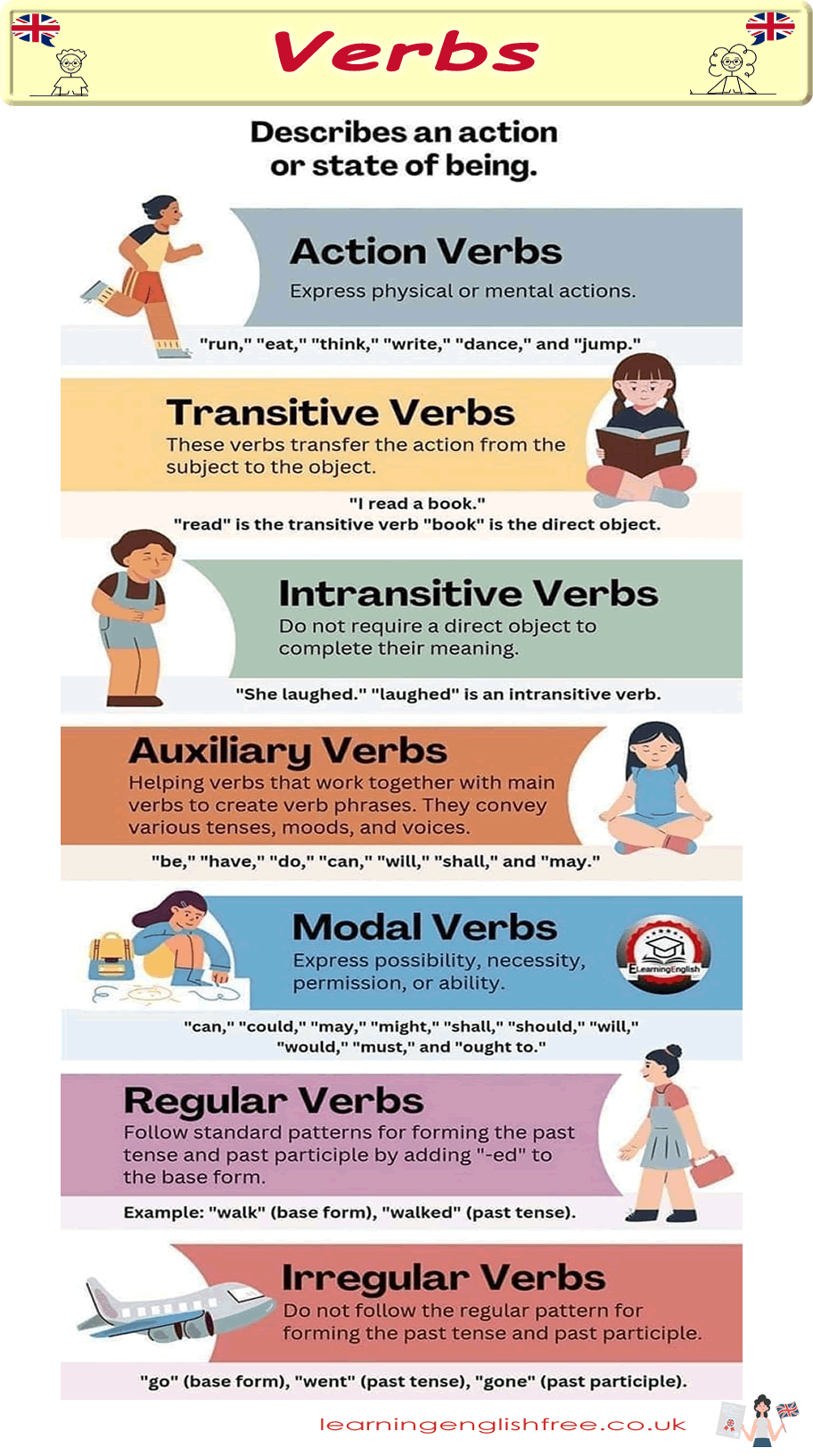
Verbs: The Action and State of Being
- Verbs describe an action or a state of being, giving life to the nouns that perform these actions or embody these states.
Action Verbs: The Movers and Shakers
- Action Verbs express physical or mental actions. They are the engines of our sentences, propelling them forward with energy and purpose.
- Run: She runs every morning to stay fit.
- Eat: I eat breakfast at 7 a.m. every day.
- Think: He thinks deeply about life's mysteries.
- Write: We write essays to improve our writing skills.
- Dance: They dance with joy at the festival.
- Jump: The cat jumps onto the windowsill to watch birds.
Transitive Verbs: The Connection Makers
- Transitive Verbs transfer the action from the subject to the object, creating a direct link between the two.
- Read: I read a book on philosophy. ("Read" transfers the action to "book".)
Intransitive Verbs: The Independent Players
- Intransitive Verbs do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. They stand alone, complete in their action or state.
- Laugh: She laughed at the joke. ("Laughed" does not need an object to make sense.)
Auxiliary Verbs: The Helpers
- Auxiliary Verbs work alongside main verbs to form complex verb phrases, expressing nuances of tense, mood, and voice.
- Be: I am running late. ("Am" helps to form the present continuous tense.)
- Have: We have finished our work. ("Have" helps to form the present perfect tense.)
- Do: Do you think so? ("Do" helps to form questions in the present tense.)
Modal Verbs: The Expressers of Modality
- Modal Verbs express possibility, necessity, permission, or ability, adding a layer of meaning to the main verb.
- Can: I can swim. (Ability)
- Must: You must see this movie. (Necessity)
- May: May I leave early today? (Permission)
Regular Verbs: The Predictable Pattern Followers
- Regular Verbs adhere to a simple pattern for forming the past tense and past participle by adding "-ed" to the base form.
- Walk: Yesterday, I walked in the park. ("Walked" follows the regular pattern.)
Irregular Verbs: The Rule Breakers
- Irregular Verbs defy the standard pattern, each following its unique path to the past tense and past participle.
- Go: Last year, we went to France. (Goes from "go" to "went", breaking the regular pattern.)
Conclusion: Unveiling the Power of Verbs
Summary and Takeaways
Understanding the diverse world of verbs is crucial for mastering the English language. Through this lesson, we've explored the various types of verbs, each serving a unique function in our language. From expressing actions and states of being with action verbs to indicating relationships between subjects and objects with transitive and intransitive verbs, and from assisting main verbs with auxiliary verbs to expressing nuances with modal verbs, we've covered the fundamental aspects of English verbs. Additionally, recognizing the difference between regular and irregular verbs helps learners navigate the complexities of verb conjugation.
Tips for Remembering
To retain what we've learned, consider employing memory aids such as drawing pictures related to verbs, creating mind maps of verb types, or leaving sticky notes around your study area with verb examples. Incorporating these verbs into daily conversation and writing will also solidify your understanding.
Real-Life Applications
Applying these concepts in real-life situations enhances learning. Whether reading a book, watching a film, or engaging in conversation, pay attention to the verbs used and try to identify their types and functions. This active engagement with the language will make learning more meaningful and enjoyable.
Encouragement to Share and Connect
We invite you to share your learning journey with others. Visit our Facebook page at www.facebook.com/learningenglishfree.co.uk for more lessons and tips. Engaging with a community of learners can provide additional support and motivation.
Remember, mastering verbs is a step toward fluency in English. Keep practicing, remain curious, and enjoy the process of learning.
