Understanding Active and Passive Voice: Verb Forms Explained
Active Voice
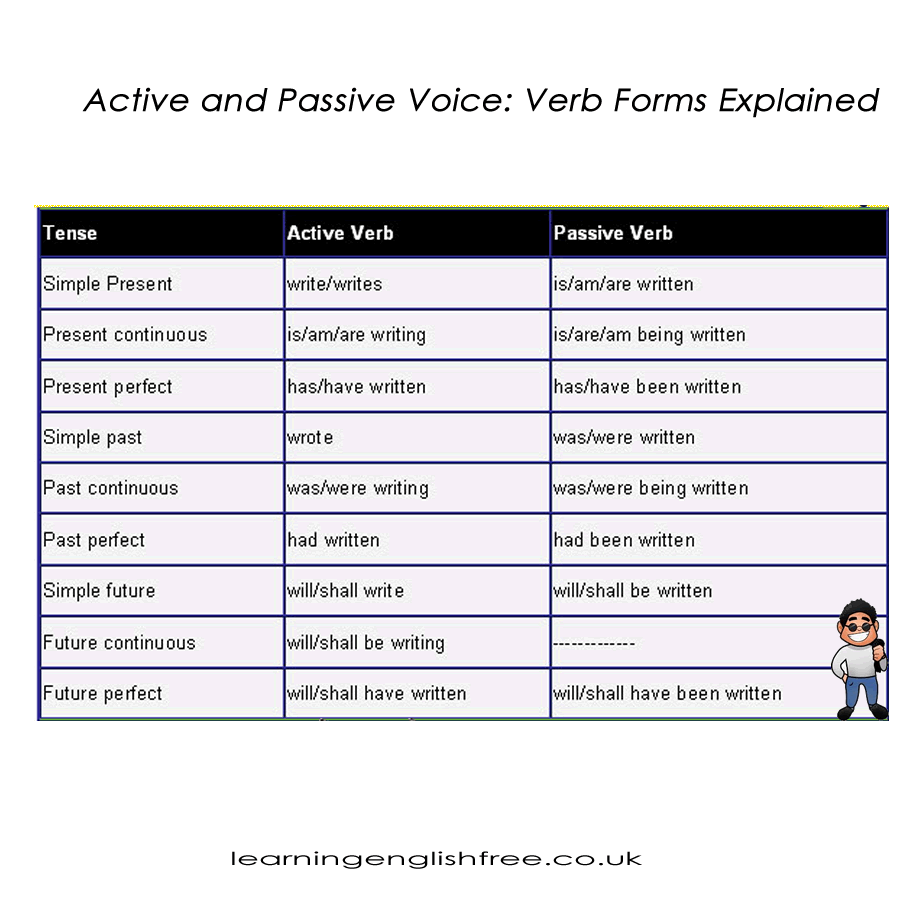
- Simple Present: write/writes
- Present Continuous: is/am/are writing
- Present Perfect: has/have written
- Simple Past: wrote
- Past Continuous: was/were writing
- Past Perfect: had written
- Simple Future: will/shall write
- Future Continuous: will/shall be writing
- Future Perfect: will/shall have written
Passive Voice
- Simple Present: is/am/are written
- Present Continuous: is/are/am being written
- Present Perfect: has/have been written
- Simple Past: was/were written
- Past Continuous: was/were being written
- Past Perfect: had been written
- Simple Future: will/shall be written
- Future Perfect: will/shall have been written
Each verb form is categorized based on whether it's used in an active or passive construction. Active voice is when the subject performs the action of the verb, and passive voice is when the subject is acted upon by the verb.
Examples of active and Passive Voice: Verb Forms
Active Voice
-
Simple Present (write/writes): Used for regular actions or facts.
Example: "She writes emails every day." -
Present Continuous (is/am/are writing): Used for actions happening right now or around now.
Example: "I am writing a letter." -
Present Perfect (has/have written): Used for actions that happened at an unspecified time before now.
Example: "He has written three books." -
Simple Past (wrote): Used for actions completed in the past.
Example: "They wrote a report yesterday." -
Past Continuous (was/were writing): Used for actions that were ongoing in the past.
Example: "We were writing essays all evening." -
Past Perfect (had written): Used for actions that were completed before another past action.
Example: "She had written the email before the computer crashed." -
Simple Future (will/shall write): Used for actions that will happen in the future.
Example: "I will write a novel one day." -
Future Continuous (will/shall be writing): Used for actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
Example: "Tomorrow at this time, I will be writing my exam." -
Future Perfect (will/shall have written): Used for actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
Example: "By next year, he will have written his thesis."
Passive Voice
-
Simple Present (is/am/are written): Used for regular actions or facts, focusing on the receiver of the action.
Example: "The book is written in simple English." -
Present Continuous (is/are/am being written): Used for ongoing actions happening now, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The report is being written by the team." -
Present Perfect (has/have been written): Used for actions completed at an unspecified time before now, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The novel has been written by a famous author." -
Simple Past (was/were written): Used for actions completed in the past, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The letter was written yesterday." -
Past Continuous (was/were being written): Used for ongoing past actions, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The essay was being written when the power went out." -
Past Perfect (had been written): Used for actions completed before another past action, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The email had been written before the system crashed." -
Simple Future (will/shall be written): Used for actions that will happen in the future, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The book will be written by next year." -
Future Perfect (will/shall have been written): Used for actions that will be completed before a specific future time, focusing on the receiver.
Example: "The project will have been written by the end of the month."
These examples illustrate how each verb form is used in sentences, with the focus either on the subject performing the action (active voice) or on the subject receiving the action (passive voice).
