What are modal verbs?
Today, we will explore modal verbs, an essential part of English grammar. Modal verbs are special verbs that add meaning to the main verb in a sentence. They can express abilities, permission, possibility, obligation, or necessity. Understanding modal verbs is vital in speaking and writing English well.
In the following lists, you'll learn modal verbs like 'can', 'must', 'should', and more. Three simple examples will accompany each verb to show how it's used in everyday situations. These examples will help you grasp the nuances of each modal verb, making your English communication more transparent and precise. By the end of this lesson, you'll better understand how to use these essential verbs in different contexts.
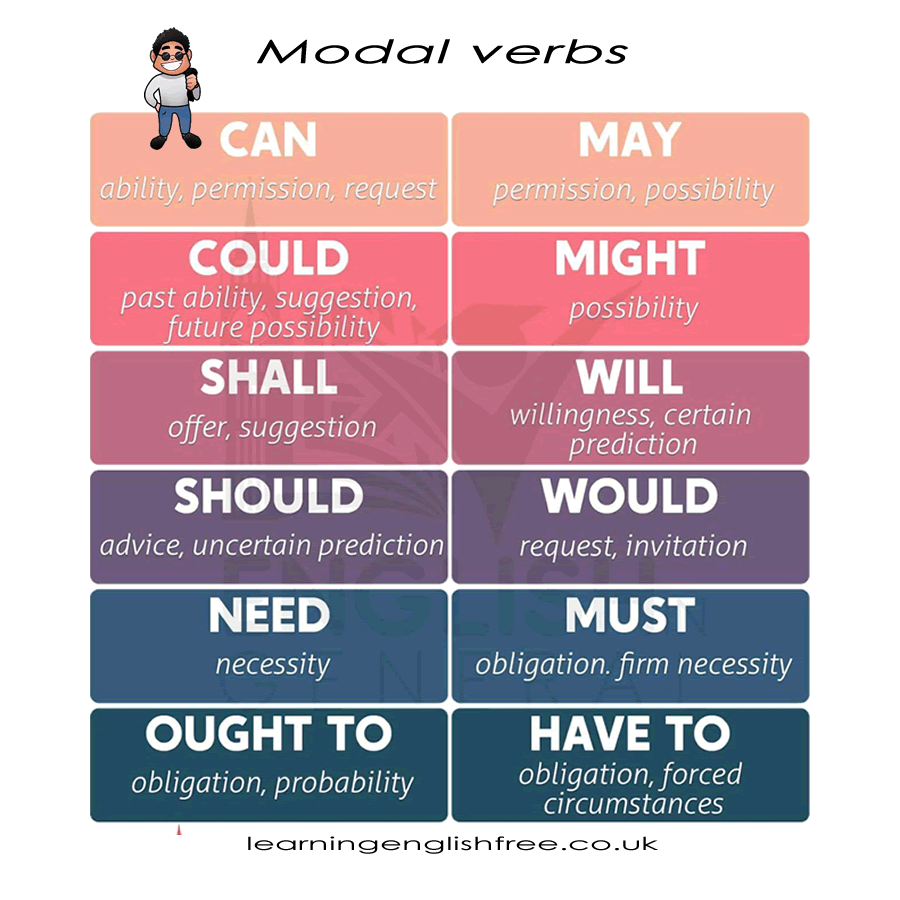
- CAN - Ability, Permission, Request
- COULD - Past Ability, Suggestion, Future Possibility
- SHALL - Offer, Suggestion
- SHOULD - Advise, Uncertain Prediction
- NEED - Necessity
- OUGHT TO - Obligation, Probability
- MAY - Permission, Possibility
- MIGHT - Possibility
- WILL - Willingness, Certain Prediction
- WOULD - Request, Invitation
- MUST - Obligation, Firm Necessity
- HAVE TO - Obligation, Forced Circumstances
How to use modal verbs correctly
-
CAN: Used when you can do something, ask or give permission, or make a request. Example: "Can I open the window?"
-
COULD: Refers to something you were able to do in the past, a polite suggestion, or something that might happen in the future. Example: "I could swim when I was six."
-
SHALL: Often used in questions to make an offer or a suggestion. Example: "Shall we go to the park?"
-
SHOULD: Used to give advice or say what is the right thing to do, and also when you think something is likely to happen. Example: "You should wear a coat."
-
NEED: Expresses necessity but is less intense than "must". Example: "You need to eat to stay healthy."
-
OUGHT TO: Similar to "should", it's used to suggest what is the right or best thing to do. Example: "You ought to apologize."
-
MAY: Used to ask for or give permission and to say something is possible. Example: "May I use your phone?"
-
MIGHT: Used when saying something is possible but not sure. Example: "It might rain today."
-
WILL: Expresses willingness, a promise, or something that is certain to happen. Example: "I will help you with your homework."
-
WOULD: Used to ask for something or invite someone politely. Example: "Would you like some tea?"
-
MUST: Indicates a vital necessity or obligation. Example: "You must stop at a red light."
-
HAVE TO: Used to express obligation, especially when imposed by someone else or a rule. Example: "I have to wear a uniform to school."
How to use modal verbs in a sentence
-
CAN (ability, permission, request)
- "I can speak Spanish."
- "Can I borrow your pen?"
- "You can go to the party after finishing your homework."
-
COULD (past ability, suggestion, future possibility)
- "When I was young, I could run very fast."
- "You could try calling customer service for help."
- "It could rain tomorrow, so take an umbrella."
-
SHALL (offer, suggestion)
- "Shall I open the window?"
- "Shall we start the meeting now?"
- "What shall we have for dinner?"
-
SHOULD (advise, uncertain prediction)
- "You should drink more water."
- "I should be home by 8 PM."
- "You should see a doctor if the pain continues."
-
NEED (necessity)
- "You need to wear a helmet when riding a bike."
- "We need to clean the house before they arrive."
- "She needs to finish her homework before watching TV."
-
OUGHT TO (obligation, probability)
- "You ought to apologize for your mistake."
- "He ought to be here by now."
- "They ought to take better care of their health."
-
MAY (permission, possibility)
- "May I leave early today?"
- "You may see wildlife on your hike."
- "May I use your computer?"
-
MIGHT (possibility)
- "I might go to the party if I finish work early."
- "She might know the answer."
- "They might be able to help us."
-
WILL (willingness, specific prediction)
- "I will help you with your project."
- "It will be sunny tomorrow."
- "Will you be coming to the meeting?"
-
WOULD (request, invitation)
- "Would you like some coffee?"
- "Would you help me with this?"
- "I would like to book a table for two."
-
MUST (obligation, firm necessity)
- "You must stop at a red light."
- "We must follow the rules."
- "I must remember to call my mom."
-
HAVE TO (obligation, forced circumstances)
- "I have to go to work early tomorrow."
- "She has to wear glasses for reading."
- "They have to complete the project by Friday."
